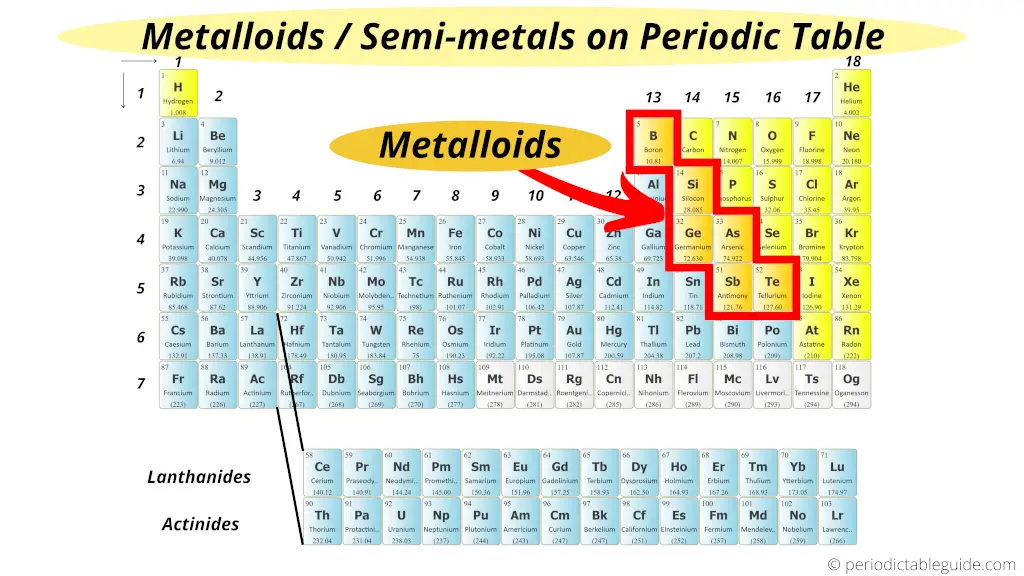
Metalloids Are . most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional electrical conductors and display nonmetallic chemical properties. covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Metalloids have semiconductor properties and form amphoteric oxides. There are 6 elements in this group [1]. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. the metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium. a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance. Metalloids can also be called semimetals.
from periodictableguide.com
most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional electrical conductors and display nonmetallic chemical properties. the metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium. There are 6 elements in this group [1]. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Metalloids can also be called semimetals. a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Metalloids have semiconductor properties and form amphoteric oxides. metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance.
Where are Metalloids located on the Periodic table? (Images)
Metalloids Are In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Metalloids can also be called semimetals. a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. There are 6 elements in this group [1]. metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance. the metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium. covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Metalloids have semiconductor properties and form amphoteric oxides. most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional electrical conductors and display nonmetallic chemical properties.
From www.pinterest.com
5 Examples of Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals Metals Nonmetals Metalloids Are Metalloids have semiconductor properties and form amphoteric oxides. most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional electrical conductors and display nonmetallic chemical properties. covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance. the. Metalloids Are.
From thechemistrynotes.com
Metalloids Definition, Properties, Uses, and Applications Metalloids Are the metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium. There are 6 elements in this group [1]. a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance. Metalloids have semiconductor properties and. Metalloids Are.
From brainly.in
name the metal ,metalloids and non metals in the first 20 elements Metalloids Are There are 6 elements in this group [1]. covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Metalloids have semiconductor properties and form amphoteric oxides. most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional electrical conductors and display nonmetallic chemical properties. Metalloids can also be called semimetals. In this regard, these elements resemble. Metalloids Are.
From newtondesk.com
Metalloids (Periodic Table) Properties, Uses, & Facts Metalloids Are Metalloids can also be called semimetals. metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance. most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional electrical conductors and display nonmetallic chemical properties. Metalloids have semiconductor properties and form amphoteric oxides. covalent bonding is the key to the crystal. Metalloids Are.
From byjus.com
How many metals, metalloids and nonmetals are there in the third period Metalloids Are a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance. Metalloids can also be called semimetals. There are 6 elements in this group [1]. the metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and. Metalloids Are.
From brokeasshome.com
Metalloids Located On The Periodic Table Metalloids Are In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. the metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium. a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional electrical conductors and display nonmetallic chemical properties. metalloid, in chemistry,. Metalloids Are.
From blog.thepipingmart.com
Metalloids Uses and Properties Metalloids Are the metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium. Metalloids can also be called semimetals. covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional. Metalloids Are.
From www.animalia-life.club
Periodic Table With Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids Metalloids Are a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. Metalloids can also be called semimetals. most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional electrical conductors and display nonmetallic chemical properties. metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple. Metalloids Are.
From pediabay.com
Periodic Table Metals, Nonmetals & Metalloids Pediabay Metalloids Are metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. the metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium. a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. There are 6 elements in. Metalloids Are.
From cabinet.matttroy.net
Periodic Table Metalloids Line Matttroy Metalloids Are most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional electrical conductors and display nonmetallic chemical properties. metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance. Metalloids can also be called semimetals. There are 6 elements in this group [1]. a metalloid is an element that has properties. Metalloids Are.
From sciencetrends.com
4 Properties Of Metalloids Science Trends Metalloids Are most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional electrical conductors and display nonmetallic chemical properties. There are 6 elements in this group [1]. the metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Metalloids can also be called semimetals. covalent bonding is the key to the. Metalloids Are.
From sciencenotes.org
List of Metalloids or Semimetals Metalloids Are metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance. most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional electrical conductors and display nonmetallic chemical properties. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. There are 6 elements in this group [1]. a metalloid is an element that. Metalloids Are.
From sciencenotes.org
Metalloids Science Notes and Projects Metalloids Are metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance. covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Metalloids have semiconductor properties and form amphoteric oxides. There are 6 elements in this group [1]. a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between. Metalloids Are.
From www.differencebetween.com
Difference Between Metals and Metalloids Compare the Difference Metalloids Are a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. There are 6 elements in this group [1]. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional electrical conductors and display nonmetallic chemical properties. the metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium,. Metalloids Are.
From periodictableguide.com
Periodic table labeled with Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Metalloids Are Metalloids can also be called semimetals. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Metalloids have semiconductor properties and form amphoteric oxides. covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. most metalloids have a shiny, metallic appearance but are brittle, unexceptional electrical conductors and display nonmetallic chemical properties. the metalloids are boron, silicon,. Metalloids Are.
From www.faqs.com.pk
What Are Metalloids? FAQs Metalloids Are the metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium. a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. Metalloids have semiconductor properties and form amphoteric oxides. There are 6 elements in this group [1]. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. covalent bonding is the key to. Metalloids Are.
From www.youtube.com
Periodic Table Metals, Nonmetals, Metalloids YouTube Metalloids Are covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. the metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium. Metalloids can also be called semimetals. There are 6 elements in this group [1]. a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. metalloid, in chemistry,. Metalloids Are.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Metals, Nonmetals and Metalloids PowerPoint Presentation, free Metalloids Are Metalloids can also be called semimetals. covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance. Metalloids have semiconductor properties and form amphoteric oxides. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. There are 6 elements in this group. Metalloids Are.